🛫 Intro
Over 7% of oil products are consumed by the global aircraft fleet (276 million tons of jet fuel) and 2.7% of CO2 emissions are a direct result of in-flight consumption. The aerospace industry will have to develop innovative new ways to reduce CO2 as countries and governments around the world take action to reduce CO2, as well as develop products and services that meet the needs of customers, both in the private aerospace market and in the public aviation market.
Our goal in this post is to review 10 aerospace industry trends that will be relevant in 2023 and 2024. In order to qualify or validate much of the information that we will be reviewing, we will start the post with a section on market research. Now let’s get started…

📜 Table of contents
🏷️ Tags:
aerospace; air transport; aerospace market research; air transport market research; aerospace engineering; aerospace companies ; supersonic flight (SST); aerospace innovations
💹 2023 Aerospace Market Research
During the COVID-19 pandemic of 2020, many speculated that the airline industry would be among the first industries to suffer acute damage due to the decline in demand. By EOY 2020, the travel industry suffered a net loss of -140 billion USD due to travel-related restrictions. The silver lining for 2022 - 2023, is the overall recovery that the industry has experienced, resulting in projected net profits, despite a now secondary looming crisis as central banks continue to raise rates. Many analysts and economists have already priced in a potential recession.
Although that being said, there are a few other macro themes worth highlighting because they either directly or indirectly affect the aerospace industry in general.
🗺️ Aerospace geopolotics and macro
Specifically within the air-transportation sub-industry, the ongoing war in Eastern Europe has greatly affected global oil prices and caused further volatility, resulting in both supply-side and demand-side shocks. There is also a demand crunch resulting from reduced travel in and out of Eastern Europe which is a cause for concern for any airline that has a large chunk of its fleet stationed in this region.
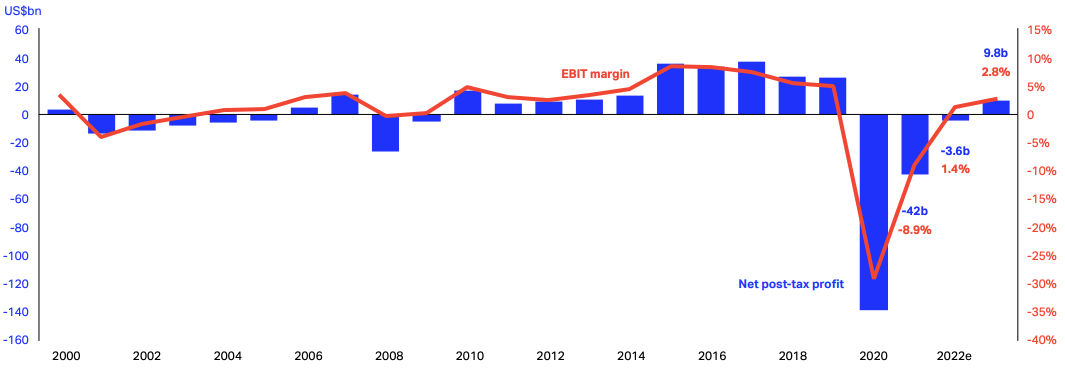 |
| Source: IATA Economic Report - EBIT margin and Net post-tax profit |
🌌 Aerospace growth in 2022
In 2022, the aerospace industry is expected to have a robust economic outlook. The International Air Transport Association (IATA) projects that the aerospace industry will grow by more than 5% in 2022, while airlines will see a 6.6% increase. Global passenger numbers are also projected to reach 4.6 billion in 2022, an increase of over 5.3% from 2021.
🌠 Aerospace growth projection 2023
According to IATA, the aerospace industry is projected to grow by 3.2% in 2023, while airlines are expected to grow by 4.1%. More than 4.8 billion passengers are expected in 2023, up 5.9% from 2022.
📊 Aerospace economic outlook
In general, the aerospace industry’s economic outlook looks positive for both 2022 and 2023. The global economy is expected to recover from the pandemic, and airlines and other companies will invest in new technologies, services, and strategies to improve efficiency and customer service. EBIT or operating margin for the industry is expected to be 0.4% in 2023, based on the 2022 and 2023 IATA forecasts.
🛰️ 🧑🚀 10 aerospace trends and Innovations for 2023
1. CRM Rise Engines 🚁
As an open-rotor aircraft, CRMs utilize hydrogen fuel as well as sustainable fuels for propulsion. In comparison with traditional rotor-based aircraft, their core value proposition is that they are 20% more efficient.
Since the 1980s, open rotor technology has steadily developed. In order to reach the mass market, their initial design needed to be larger. Researchers and engineers have made improvements in material sciences and digital modeling to reduce the size, weight, and noise limitations of some of the nascent designs.
“RISE features a single rotating fan, with variable pitch carbon-fiber blades, behind which sits a row of static guide vanes. Safran’s earlier Sage2 demonstration featured a contra-rotating second fan stage, but that required “complicated internal structures which were very heavy”, says Dijoud.”
2. Additive manufacturing 🖨️
The aerospace industry has become increasingly dependent on additive manufacturing and 3D printing for both research and development and component manufacturing. Aerospace was actually one of the first industries to embrace additive manufacturing as a key business objective. Take any of the most recent commercial aircraft, and there are more than 1000 3D-printed parts. As a result of the high barrier to entry caused by the cost of this technology, most organizations cannot use it effectively as part of their R&D or manufacturing processes.
In spite of this, in the past ten years or so, some of these industrial-sized 3D printers have become cheaper to operate and smaller in size, thus expanding their potential customer base beyond the larger heavy hitters in the field to include both the smaller startup companies and larger corporations.
Public and private space companies such as SpaceX use 3D printing extensively within the space sub-industry more broadly. As I recently pointed out in my post covering military and defense industries more broadly, I made an argument that basically states, imagine a world where 3D printing can create replacement mechanical components at the battle arena, or a military surgeon can 3D print vital organs. The same argument or assumption can be applied to the space industry. For a moment, imagine a world where 3D printing can be used to create replacement parts on the space station or in space. The use case highlighted here illustrates one of the greatest tools for ensuring the success of a mission and providing astronauts with further safety.
3.Supersonic flight (SST) 💥
In the years following the collapse of the Concord in 2003 ( final launch 24 October 2003), a number of companies are attempting to solve supersonic flight for the mass market in an economically viable way with NASA’s support and other research-based institutions around the world. The value proposition of supersonic flight (SST), or flight faster than the speed of sound, is very unique; A three-hour trip between NYC and London or Paris would add value to society and businesses.
Denver-based Boom Sonic has been working to solve this problem. Designed to travel at Mach 1.7 (1,000 kn; 1,800 km/h), with a range of 4,250 nmi (7,870 km), Boom Overture is set to launch in 2029, with multiple units already allocated by companies.
Boom raised $51 million in venture capital in 2016, and an additional $100 million by January 2019. Boom technology was incubated by YCombinator in the beginning. A large-scale manufacturing facility occupying 400,000 square feet (37,161 m2) in Greensboro, North Carolina, is planned for the company to continue its mission of bringing supersonic flight to the masses.
4. Electric flight and propulsion ⚡
Electric propulsion architecture can be classified into four types: all-electric, series hybrid electric, parallel hybrid electric, and turboelectric. Of the four different classifications, each has its own advantages, including an advantage in terms of fuel consumption and weight, as well as aeronautical flight capabilities and propulsion capabilities. However, each type of aircraft also has its own disadvantages…
Helicopters, for example, are more expensive to maintain and more difficult to fly than fixed-wing aircraft. The point is that we can only design systems or complex machines by removing as much complexity as possible while addressing a specific pain point or business objective. Aerospace manufacturers will always have to make tradeoffs when deciding what is the most optimal propulsion system that generates a sufficient amount of thrust while burning as little fuel as possible.
There are a number of limitations and challenges associated with electric propulsion in the commercial aviation industry. For example, and beyond some of the pain points already discussed, the weight limitation of electric plans, a lack of infrastructure for aircraft battery charging, and the need to charge electric aircraft too frequently between flights, which is a significant limitation for commercial aviation, at the moment.
Globally, the electric aircraft market was valued at $8.5 billion in 2021 and is expected to reach $23.5 billion by 2031, growing at a CAGR of 10.9%.
5. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML)🤖
When it comes to innovation and technology, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), advanced robotics, and automation seem to be the buzzwords of most industries, especially with the rise of generative and large language models. From design to engineering, this new wave of innovations will solve problems across all industries and departments. As a result, the aerospace industry is set to undergo massive changes in the near future.
A number of aerospace companies are utilizing artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to solve business and customer problems, including enhancing customer experiences (CX) by providing the best flight options and reducing operating costs for companies that manage these often complex fleets of aircraft. Increasing safety by detecting mechanical failures preemptively with machine learning solutions, which also prevents downtime caused by maintenance issues or two additional areas of focus for AI and ML in aerospace.
Another major use case for AI and ML is autonomous aircraft, which could reduce human error and pilot stress. In the post-covid era, staffing concerns have been a major pain point for most industries, and new often AI-based solutions will be needed to compensate.
The market size for AI and ML within the aerospace industry is expected to reach $7.35 billion USD by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 14.1% from 2020 to 2027.
6. Network Innovations and IoT 🌐
The main value propositions for IoT within aerospace are lower operating costs, predictive maintenance scheduling, as well as security for the end passengers via software optimizations.
A more interconnected network and fleet of aircraft are both massive value adds to the businesses operating the aircraft, and the end users who are flying in them. IoT-enabled aircraft will allow businesses to methodically track all maintenance activities against the operating conditions/ parameters of the aircraft themselves. IoT can also result in optimizations for the end users flying in airplanes via better in-air connectivity and networks.
During the forecast period, “IoT in Aviation” is expected to grow at a CAGR of 19.2 percent to reach USD 6.40 Billion by 2029. In 2022, the market size was USD 1.57 Billion, based on data presented in a report by GlobeNewswire.
7. New materials 🪨
Materials such as carbon fiber have made it technically feasible to create more complex shapes using composite materials that would not have been possible with machined parts. For approximately a century, the aerospace industry used aluminum whereas today, roughly only 20% of an airplane is made with aluminum. Titanium has also been leveraged to create both interior and structural components within aerospace. Titanium was discovered in 1791 and has been used extensively in manufacturing since. It wasn’t until the start of the Cold War that it began its journey into both the military and commercial aerospace industries. Today, the aerospace industry is the number one customer for titanium alloy products.
CFRPs (Carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers) are used primarily for non-structural components such as interior components within commercial aerospace, but within military applications, CFRPs are used throughout vehicles, which includes structural components. Composites, nano partials, and Graphene are three examples of materials that are being used to optimize different aspects of aerospace material design and development.
The global aerospace composites market is expected to be valued at USD 51.6 billion by 2027.
8. Blockchain and decentralized ledger technologies (DLT) 🔐
There are many use cases for decentralized ledgers beyond crypto, although blockchain and decentralized ledger technologies are primarily associated with cryptocurrency. In the aerospace industry, blockchains are being used to improve aircraft maintenance and scheduling. There are several benefits to having an immutable ledger. For starters, removing the need for a database and spreadsheets will optimize costs long-term and lead to better maintenance outcomes.
Other areas where blockchain could be used include asset tracking and traceability, inventory management, and contract management. Blockchain technology can also be used to securely store and transfer data, create trustless systems, and facilitate secure payments, all of which represent pain points for those working within the aerospace industry.
9. Aerial mobility: urban air mobility (UAM) and advanced air mobility 🚁
A number of companies have promised multi-copter or passenger drones, as well as electric vertical takeoff and landing vehicles (eVOTL), for the last ten years. However, we have yet to see these technologies materialize and become viable alternatives to conventional transportation. Therefore, it would appear that society is moving towards a future where these services become more and more viable.
The UAM industry more broadly is projected to grow from $2.6 billion in 2020 to an estimated $9 billion by 2030.
10. Advanced/ improved satellite tech 👩🚀 🛰️
Recent years have seen significant advancements in satellite technology within the aerospace industry. The speed, resolution, and accuracy of data transmission allow for better and more efficient mission operations. With advanced sensors and comms tools, satellites are now able to track and monitor aircraft and other objects in the sky more precisely than ever before.
Internet access has become a critical component of any advanced economy, and when the Ukraine war broke out, Ukraine’s utility companies found themselves without access to the web. Millions of Ukrainians who were unable to access a stable connection after the war now have access to Starlink, SpaceX’s satellite-based internet service. Using the newest generation of internet-based satellites, remote and inaccessible areas can also be connected to the internet, increasing access to information and communication.
🏁 Closing Analysis
Carbon dioxide emissions from passenger jets account for 2% of annual emissions, but this percentage is expected to rise in the future. As we noted at the beginning of this post, the global aircraft fleet consumes more than 7% of oil products (276 million tons of jet fuel) and 2.7% of CO2 emissions come from inflight consumption. As a whole, the vehicles we use for transportation have become 80% more efficient over time. Each new generation of aircraft has improved efficiency by 15-20%. It is estimated that the global airline industry will spend USD 221.8 billion on fuel in 2022.
Airlines spend 30% of their budget on fuel, which drives fuel innovation, and with the advent of zero-emission fuel, biofuels with lower emissions, and sustainable aviation fuels (SAF), it is highly likely that we will continue to see new innovations in the coming years and decades that will result in lower operating costs and higher efficiency across all aspects and sub-industries of aviation.
Due to the incessant need to optimize for sustainability, as well as the continuing increase in population, aerospace will continue to see massive growth in the coming years. In addition to the 10 innovations discussed in this post, hydrogen-powered aircraft, solar-powered aircraft, and hybrid aircraft that utilize a combination of internal combustion engines and sustainable power systems are also important innovations worth pointing out.
👾 More Recent-Posts
-
Bitcoin (BTC) Revolution: Catalyst, History, and Analysis
The main goal of this piece is to gain a deeper understanding of the reasoning behind the creation of Bitcoin, allowing for a more comprehensive perspective on its future
-
Macro & Geopolotics Report: 2023 Business Trends Report
In this post, we discuss macroeconomics, as well as geopolitics as part of the 2023 Business Trends Report 🌍
-
💲NEAR Protocol: Overview and Price Prediction
In this article, we will be conducting an extensive analysis of the 💲NEAR protocol, which is the platform I have the most experience building dApps on, as a Product Manager in web3
-
8 Healthcare Industry Trends and Innovations
In this post, we will be reviewing 8 business trends for the healthcare industry, including each of it's sub-industries, such as MedTech🔬
-
Cardano(ADA) Overview and Price Prediction
As a part of this post, we'll be reviewing what Cardano (ADA) is, its benefits, Tokenomics, a price prediction model, and the future of its fledgling ecosystem 💱
-
Ruby on Rails and The Future Of MVC
Discover the amazing potential of Ruby on Rails! Learn about its history and design philosophy, why it's the perfect choice for web development, and how to get started with the framework ♦️
-
Artificial Intelligence: Business Trends Report
Large language and generative models are reaching a point of emotional realness that they can no longer be distinguished from humans 🚀
-
2023 Geopolitics Report
A guide to help both businesses and product managers use geopolitics as a strategic advantage in 2023
-
Post-Industrial Digital Banking
Explore the post-industrial era of digital banking. Deployment-based market research, post-industrial hypothesis validation,opportunities,and more 📲
-
How 👾 (AI) Will Transform Product Management
In this post, we will unpack how (AI) will transform aspects of product management, as well as it's impact across cross-functinoal teams 🎖️
-
2023 Transportation Industry Trends 🚊
In this post, we will be covering 2023 Transportation Industry Trends, including market research, business strategy, and more... 🚉
-
Energy Sector Forecast 2023 ⚡
The 2023 Business Trends Report covers sector-based projections, major innovations, market dynamics, opportunities, and technologies by sector or industry - this post covers both traditional and renewable energy markets 📈
-
To-Blog Or Not-To Blog❓ | 2023 Blog Launch Helper |
This post is designed to help you or your team launch and optimize a successful blog by examining why businesses blog, providing a blog business plan guide, exploring SEO and analytics tools, and an overview of blogging platforms and frameworks
-
Make the web fast again | What is a CDN❓| How do CDNs work❓
In this post, we review what a CDN is, how they work, the business of cdns, as well as some of the best options to consider when choosing a cdn
-
We're In Way Over Our Heads | Going Headless (CMS)
Content is king! In this post we review Headless-CMS, content management systems; How they work, an overview of JAMstack, some of the best options, etc, will be discuessed
-
Building Static Websites In An Un-Static-World (SSGs)
In this post we'll be reviewing (SSGs) static site generators, reviewing the tech as a means of providing value to your next project or business during times of uncertainty– The advantages, how they work, and evaluating frameworks, including Jekyll, Hugo, and Gatsby. JS, etc 🛠
-
How (AI) is changing the way we work
In this post, we'll explore two use cases for (AI) ⚔️ (AI) Writing and Text-To-Image (Generative-AI) – How they work, as well as their current and future, use cases for the workplace, as well as available tools and services
-
Industrial Revolutions
Part-1 (1-2 IR) This is the first post of the Industrial Revolution series, covering the 1st and 2nd Industrial Revolutions, major tech innovations and advancements during each period
-
Industrial Revolutions
Part-2 (3-4 IR) This is the second and final post of the Industrial Revolutions series, covering the 3rd and 4th Industrial Revolutions. Focusing on the tech and innovations during this period
-
Tokenomics
Ledgers and Accounting represent two foundational aspects of tokenomics and token-engineering, this is the first of many post where I will be covering tokenomics, focusing on presenting my research and aspects of system design
-
Fintech Deep-dive
How the tech industry is changing finance: This post outlines the history of financial technology (FinTech) and major innovations, as well as companies at the forefront of this sector
-
Web 3 Systemic Issues Report
In this post I review some of the most systemic-issues that I have identifed after contributing to a few web3 startups in varying levels of involvement – please take what is stated as speculative conjecture, nothing more 🙏