🌃 Intro
In my post, We’re in way over our heads, Going headless-CMS , I explored how headless-CMS can benefit your project or business during these unpredictable times. This time, we’re focusing on CDNs and how they can improve customer experience by boosting speed.
CDNs can deliver page content up to 70% faster, leading to increased customer acquisition, revenue, and retention, reduced bounce rate, and increased engagement. In this post, we’ll cover what CDNs are, how they work, how companies such as Netflix have leveraged them, and the best CDN options available.

What is a CDN; How do CDNs work?; Data Center; Networking; Microservice;
📖 Learning Objectives & Contents
🌄 Building Empathy: My passion for building EconmyBlocked grew during the last three months. Initially, users were accessing resources from my hosting provider’s origin server, which caused slow response times. My goals for V0.5 were straightforward.
Build a solid foundation, while developing a better understanding of the technical and business blog market, defining my niche, optimizing for performance, and core web vitals, SEO included. As a result of using a CDN service, core web vitals improved, latency decreased, and web traffic increased for the first month.
📸 What is a CDN?
CDNs are systems of distributed servers that deliver web content to users based on their geographic location from data centers known as Points-Of-Presence (POCs), which represent the individual nodes at the edge that make up the network itself.
By caching content or data locally at edge locations, CDNs allow websites and other content providers to deliver static and dynamic content, including webpages, images, videos, and streaming media, more quickly and reliably. CDNs deliver content with high availability and performance closer to the location where the client device requests access.
Let’s briefly review the business model for CDN providers before reviewing the technical specifications.
💡 CDN Business model
Internet service providers (ISPs) provide servers for storing static and dynamic content, such as images, HTML pages, JavaScript, CSS, SASS, videos, and text.
A CDN provider like Cloudflare or Fastly manages the servers storing the CDN business logic in data centers on behalf of end users. Usually, CDN providers charge based on how much data they transmit, how many users they have, and/or the user’s geographic region.
Pricing ranges from $25 USD per month for low-traffic sites to tens of thousands of USD per month for companies with large customer bases, distributed worldwide. Hosting companies also benefit from the extra storage and data traffic.
🎆 How Does CDN Work? | The Technical Spec
Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are geographically dispersed servers that deliver content quickly, by caching it closer to end-user requests. Multiple servers (POCs) cache dynamic & static content such as images, HTML pages, javascript, CSS, JS, videos, and text– Reducing the amount of time it takes to fetch contents from the host web server, reduces latency and improves the end-user experience.
Internet exchange points (IXPs) are the physical locations where ISPs and CDN providers unite to share resources, distributed across multiple networks. Users can access content more quickly if data is exchanged at the edge, which routes traffic between networks, rather than if they were requesting content from your origin web server.
IXPs are layer-2 LANs utilizing the OSI network model to enable networks to connect with one another. In the technical stack, these processes are located at the network layer. By comparing an IXP to a home network, we can better understand and compare what an IXP is, with the only core difference being its scale.
By connecting CDNs to these locations, you are able to take advantage of the speed that CDNs offer by delineation, interconnected by a high-speed geographical routing network, and caching your data or content at these locations, which allows it to be served to your end users more quickly.
CDNs are a must-have for many industries, offering improved speed and reliability. For example, audio, videos, and movies are delivered via CDNs in the entertainment sector, while gaming businesses benefit from reduced latency, and increased performance, through caching content to be downloaded or streamed to end users, as well as for game patches, gaming businesses gain reduced latency and increased performance. Those who serve high-resolution media: video and audio, to their customers, may be interested in knowing which CDN Netflix uses…
🎬 Which CDN does Netflix use? | Special Attention
Netflix’s proprietary CDN, Open Connect CDN, delivers high-resolution video and audio to a massive customer base concurrently. Netflix CDN consists of a variety of servers, including edge servers, origin servers, and content delivery servers. The edge servers are situated near the user’s location and store the most frequently requested content. The origin servers are located in data centers and are the source of the content. Servers that deliver content to users are located between edge and origin servers.
Caching, data replication and streaming protocols are also used by Netflix to optimize the delivery of content. Caching involves storing frequently requested content near the user, whereas data replication ensures that content is always available. Additionally, Netflix uses streaming protocols like HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP (DASH) to ensure that content is delivered quickly and reliably.
In 2015, their strategic infrastructure goal was to “get more and more gigabits per second from a single box”, a trend that has continued to this day. Back in 2015, the company as a whole was experiencing peak growth, so each server box needed to handle as many subscribers as possible in order to meet demand.
Netflix works directly with ISPs to deliver content more efficiently with its Netflix OpenConnect Program, a partnership between Netflix and ISPs designed to ensure the best viewing experience for end users and to reduce ISP costs. A new trend has emerged in recent years to develop strategic relationships between content providers and networks, a model with the goal of continuous improvement for both the network (ISP) and the content provider (Netflix). Direct connections between Open Connect and residential ISPs deliver approximately 95% of Netflix traffic in 2022.
In the media industry as a whole, this approach to continuous innovation is adapted from Agile and SCRUM playbooks. ISP partners who have deployed Netflix servers within their own networks have reportedly saved $1.2B through this program alone. Once again, to ensure the highest level of quality for end users, and to reduce costs for the ISPs, a clear value adds for all parties involved.
Netflix’s greatest asset and the most expensive bucket is content, which drives the internet, and, as the saying goes, content is king! - They also have strong UI/UX and network infrastructure, teams. The competition cannot compete with their engineering-first approach to a content-driven business and their products and services set the industry standard.
Now let’s pivot back to reviewing more individual use cases for CDNs per industry:
The eCommerce industry uses CDNs to deliver high-resolution product images, videos, and other content needed to make informed purchases.
The education industry uses CDNs to deliver educational content such as lectures, presentations, and videos. Furthermore, CDNs are used to deliver patient records and other information securely, with speed, and enhanced security in the healthcare industry.
It is important to use a CDN that is best suited to serve your customer base wherever they are located, as part of your network infrastructure strategy. This is where technical feasibility and discovery come into play.
The best CDN for a product or service will be determined by testing and analyzing network speeds per CDN provider. For a small-town blog covering current events, a CDN may not be necessary, if most of your site traffic comes from one region in the US. It is logical to use a CDN if you have 40% of your customers in the US and the remaining 60% distributed globally and in multiple regions.
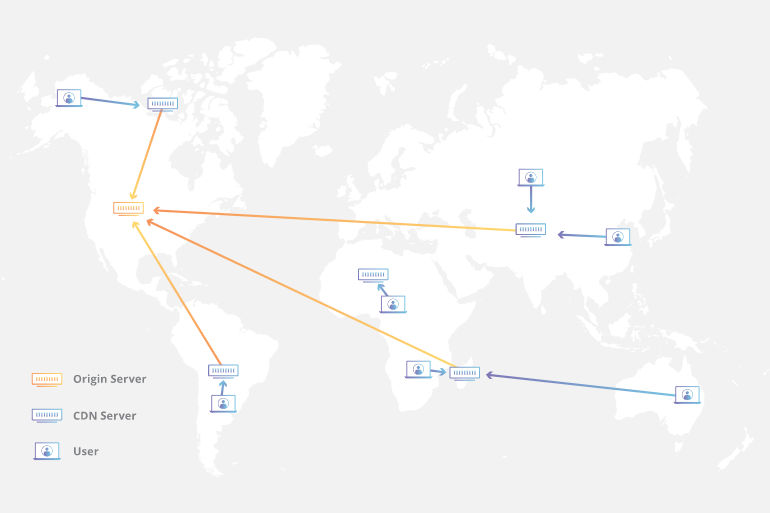 |
| Diagram Source: CloundFlare |
🔐 CDN Security Benefits
By design, a CDN in and of itself can help improve overall security by serving fresh TLS/SSL certs when end users request cached content or data from their client, originating from the edge server or POC for the CDN, ensuring that each request is encrypted to guarantee the safety of the end user.
On top of some CDN services, providers allow you to configure application profiling, which works by constantly analyzing all web traffic, to and from your site or app, and blocking applications that fail to adhere to the profile of your site or web application.
It is the same for native mobile, but its primary use case is web-based. There are some CDNs that use a signature-based model to detect malicious requests, and attack patterns, blocking them with DDoS protection; Now let’s review some of the best CDNs on the market and evaluate their unique feature sets.
🌍 Which CDN is best❓
Despite the misleading title for this section, we will only review some of the best options available today, and which is best for your unique business needs. I won’t make any absolute statements about products or services I haven’t used myself and will base my evaluation on feedback reviewed or my own experience.
1. Cloudflare CDN
Cloudflare CDN is an industry-leading website performance and security company that provides a wide range of services to help businesses improve their online presence, including content delivery networks, web application firewalls, and domain name system(DNS).
Most newer players in the space have tried to replicate their CDN because it is the industry standard for the performance and sheer scale of their networks.
2. Fastly
Fastly is an Edge cloud platform offering feature risk services within the cloud-computing space, including network services, CDN, CDN Video Streaming, Load Balancing, Image optimization, and more. Additionally, Fastly offers security features, observability, analytics, and metrics for real-time network monitoring and tracing, as well as visitor analytics.
3. Neflify
As the king of the JAMstack, Netlify offers a remote-first cloud-computing platform that enables developers to develop, deploy, and scale their applications and services more easily than traditional methods. Their proprietary CDN is deployed by default as part of their vertically integrated development and hosting stack.
In the world of cloud computing, Netlify is the king when it comes to optimizing for developers. By integrating each bucket of the deployment, hosting, and networking stack into one simple-to-use platform, Netlify has redefined the release flow for software development and technical product teams.
A few snippets of server code and a git push can generally result in a fully optimized website or application that uses a CDN by default, depending on your tech stack.
4. Securi
Securi specializes in WordPress CDN implementations, making it an under-the-radar player in the CDN market. As their strategic advantage, they offer core firewall security and enhanced security features. Through the Heroku marketplace, there is now a CDN called Expedited CDN, which represents the Securi POC network for Heroku, and can be used to cache and serve your content regardless of your technology stack hosted on Heroku.
5. Amazon CloudFront
The Amazon CloudFront content delivery network (CDN) provides secure and reliable content delivery to customers with low latency and high transfer speeds. Customers around the world use this service to quickly and securely deliver web content, including HTML pages, images, videos, and cached APIs.
Businesses can use CloudFront to improve their website’s performance, reduce latency, and reduce content delivery costs. Website performance, cost savings, and customer satisfaction (CSAT), are among the value props of the CloudFront CDN.
6. Amazon S3
Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service) is a cloud storage service from Amazon Web Services (AWS). It is an object-based storage solution that enables businesses to store and retrieve any amount of data from anywhere. S3 is secure, durable, and provides fast access to stored objects. It is also highly scalable and can be used for a variety of use cases, such as backup and archiving, disaster recovery, web hosting, and data analytics.
By combining S3 with CloudFront, you can deliver targeted, personalized, and optimized content to your customers.
7. CDN.JS
Open-source and powered by Cloudflare, CDN.JS is a free content delivery network. Currently, CDN.js is deployed on 12.5% of all websites and serves over 200 billion requests per month.
🗺️ Conclusion
From Netflix and Meta to a tech blog that has only been online for a year, CDNs offer a unique value proposition to businesses of all sizes. A correlation between site speed and revenue has made Web vitals an essential part of SEO optimization, and therefore, revenue growth.
If your business KPIs revolve around improving the customer experience, improving core web metrics, increasing site speed by decreasing latency, and improving a host of other business KPIs, implementing a CDN may be the next logical step for improving your bottom line.
The CDN discovery and technical feasibility process enable key business metrics to be correlated almost indefinitely with site speed, resulting in measurable data that can be communicated more easily by product teams, software developers, and business analysts, if necessary.
As you evaluate the right CDN for your project, company, or product, consider your unique needs and technical stack, and network infrastructure goals, and plan accordingly.
This post explains what CDNs are, how they work, including their technical specifications and implementation, as well as the proprietary CDN Netflix, uses. Can you tell me what else we learned? Additionally, we discussed the security benefits of CDNs, along with some of the top options currently available, with the goal of defining new technology implementations during times of uncertainty.
👾 More Recent-Posts
-
Bitcoin (BTC) Revolution: Catalyst, History, and Analysis
The main goal of this piece is to gain a deeper understanding of the reasoning behind the creation of Bitcoin, allowing for a more comprehensive perspective on its future
-
Macro & Geopolotics Report: 2023 Business Trends Report
In this post, we discuss macroeconomics, as well as geopolitics as part of the 2023 Business Trends Report 🌍
-
💲NEAR Protocol: Overview and Price Prediction
In this article, we will be conducting an extensive analysis of the 💲NEAR protocol, which is the platform I have the most experience building dApps on, as a Product Manager in web3
-
8 Healthcare Industry Trends and Innovations
In this post, we will be reviewing 8 business trends for the healthcare industry, including each of it's sub-industries, such as MedTech🔬
-
Cardano(ADA) Overview and Price Prediction
As a part of this post, we'll be reviewing what Cardano (ADA) is, its benefits, Tokenomics, a price prediction model, and the future of its fledgling ecosystem 💱
-
Ruby on Rails and The Future Of MVC
Discover the amazing potential of Ruby on Rails! Learn about its history and design philosophy, why it's the perfect choice for web development, and how to get started with the framework ♦️
-
Artificial Intelligence: Business Trends Report
Large language and generative models are reaching a point of emotional realness that they can no longer be distinguished from humans 🚀
-
2023 Geopolitics Report
A guide to help both businesses and product managers use geopolitics as a strategic advantage in 2023
-
Post-Industrial Digital Banking
Explore the post-industrial era of digital banking. Deployment-based market research, post-industrial hypothesis validation,opportunities,and more 📲
-
How 👾 (AI) Will Transform Product Management
In this post, we will unpack how (AI) will transform aspects of product management, as well as it's impact across cross-functinoal teams 🎖️
-
2023 Transportation Industry Trends 🚊
In this post, we will be covering 2023 Transportation Industry Trends, including market research, business strategy, and more... 🚉
-
Energy Sector Forecast 2023 ⚡
The 2023 Business Trends Report covers sector-based projections, major innovations, market dynamics, opportunities, and technologies by sector or industry - this post covers both traditional and renewable energy markets 📈
-
To-Blog Or Not-To Blog❓ | 2023 Blog Launch Helper |
This post is designed to help you or your team launch and optimize a successful blog by examining why businesses blog, providing a blog business plan guide, exploring SEO and analytics tools, and an overview of blogging platforms and frameworks
-
Make the web fast again | What is a CDN❓| How do CDNs work❓
In this post, we review what a CDN is, how they work, the business of cdns, as well as some of the best options to consider when choosing a cdn
-
We're In Way Over Our Heads | Going Headless (CMS)
Content is king! In this post we review Headless-CMS, content management systems; How they work, an overview of JAMstack, some of the best options, etc, will be discuessed
-
Building Static Websites In An Un-Static-World (SSGs)
In this post we'll be reviewing (SSGs) static site generators, reviewing the tech as a means of providing value to your next project or business during times of uncertainty– The advantages, how they work, and evaluating frameworks, including Jekyll, Hugo, and Gatsby. JS, etc 🛠
-
How (AI) is changing the way we work
In this post, we'll explore two use cases for (AI) ⚔️ (AI) Writing and Text-To-Image (Generative-AI) – How they work, as well as their current and future, use cases for the workplace, as well as available tools and services
-
Industrial Revolutions
Part-1 (1-2 IR) This is the first post of the Industrial Revolution series, covering the 1st and 2nd Industrial Revolutions, major tech innovations and advancements during each period
-
Industrial Revolutions
Part-2 (3-4 IR) This is the second and final post of the Industrial Revolutions series, covering the 3rd and 4th Industrial Revolutions. Focusing on the tech and innovations during this period
-
Tokenomics
Ledgers and Accounting represent two foundational aspects of tokenomics and token-engineering, this is the first of many post where I will be covering tokenomics, focusing on presenting my research and aspects of system design
-
Fintech Deep-dive
How the tech industry is changing finance: This post outlines the history of financial technology (FinTech) and major innovations, as well as companies at the forefront of this sector
-
Web 3 Systemic Issues Report
In this post I review some of the most systemic-issues that I have identifed after contributing to a few web3 startups in varying levels of involvement – please take what is stated as speculative conjecture, nothing more 🙏